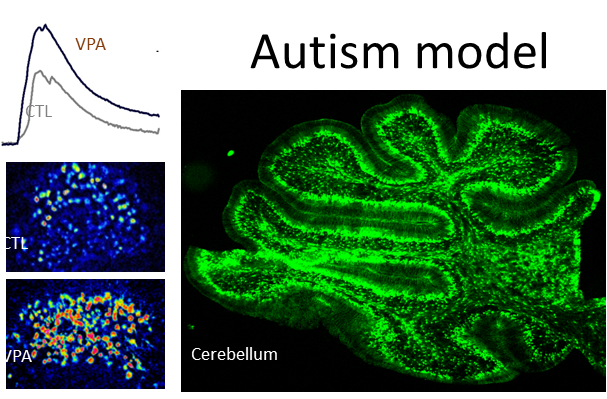
Autism spectrum disorders (ASD)
are pervasive neurodevelopmental conditions detected during childhood when delayed language onset and social deficits are observed. Children diagnosed with ASD frequently display sensorimotor deficits associated with the cerebellum, suggesting a dysfunction of synaptic circuits. Astroglia are part of the tripartite synapses and postmortem studies reported an increased expression of the glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in the cerebellum of ASD patients. Astroglia respond to neuronal activity with calcium transients that propagate to neighboring cells, resulting in a functional response known as a calcium wave. This form of intercellular signaling is implicated in proliferation, migration, and differentiation of neural precursors.
Prenatal exposure to valproate (VPA)
is a preclinical model of ASD in which premature migration and excess of apoptosis occur in the internal granular layer (IGL) of the cerebellum during the early postnatal period. We have tested calcium wave propagation in the IGL of mice prenatally exposed to VPA. Sensorimotor deficits were observed, and IGL depolarization evoked a calcium wave with astrocyte recruitment. The calcium wave propagation, initial cell recruitment, and mean amplitude of the calcium transients increased significantly in VPA-exposed mice compared to the control group. Astrocyte recruitment was significantly increased in the VPA model, but the mean amplitude of the calcium transients was unchanged. Western blot and histological studies revealed an increased expression of GFAP, higher astroglial density and augmented morphological complexity. We conclude that the functional signature of the IGL is remarkably augmented in the preclinical model of autism.